Excretory system of fishes
The excretory system is a passive biological system that removes excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body.

PPT Aquatic Life Vertebrate Animals PowerPoint Presentation ID4649263
Fish are aquatic vertebrates. They make up more than half of all vertebrate species. They are especially important in the study of vertebrate evolution because several important vertebrate traits evolved in fish. Fish show great diversity in body size. They range in length from about 8 millimeters (0.3 inches) to 16 meters (about 53 feet).
PPT Fish Anatomy, Physiology and Health PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID629827
ANATOMY OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM The excretory organ of the oyster occupies an indistinctly outlined triangular area on either side of the visceral mass. On the surface its location is marked by light hrownish pigmentation.

The excretory system of a fish Excretory System Pin TeePublic
The excretory system consists of organs which remove metabolic wastes and toxins from the body. In humans, this includes the removal of urea from the bloodstream and other wastes produced by the body. The removal of urea happens in the kidneys, while solid wastes are expelled from the large intestine. Overview

SNC2P
Figure 3.4.2 3.4. 2: In the excretory system of the (a) planaria, cilia of flame cells propel waste through a tubule formed by a tube cell. Tubules are connected into branched structures that lead to pores located all along the sides of the body. The filtrate is secreted through these pores.

Excretory Organs Fish Gill Free 30day Trial Scribd
Ammoniotelism: Ammonia Excretion. Animals that excrete their nitrogenous wastes primarily as ammonia (NH 3) are ammoniotelic. Most fish (including agnathans and most teleosts) About 80 to 90% of their nitrogenous wastes are excreted as ammonia and the remainder as urea. Goldfish (Carassius auratus)
King's Christian School Biology March 2014
The food fish, tilapia, is an extreme example, capable of adjusting to any salt concentration between freshwater and 2,000 mosm/L, twice that of seawater.. Metanephridia, another tubular excretory system, consist of internal openings that collect body fluids from the coelom through a ciliated funnel, the nephrostome, and release the fluid to.

Cuttlefish Circulatory and Excretory Systems ClipArt ETC
Control systems for fish excretion are unclear but it is expected that various hormones influence excretory homeostasis. Keywords: Excretion, Gills, rectal gland, kidney, nephrons Subject Zoology and Animal Sciences Aquatic Biology Collection: Oxford Scholarship Online Essential Fish Biology: Diversity, Structure and Function.
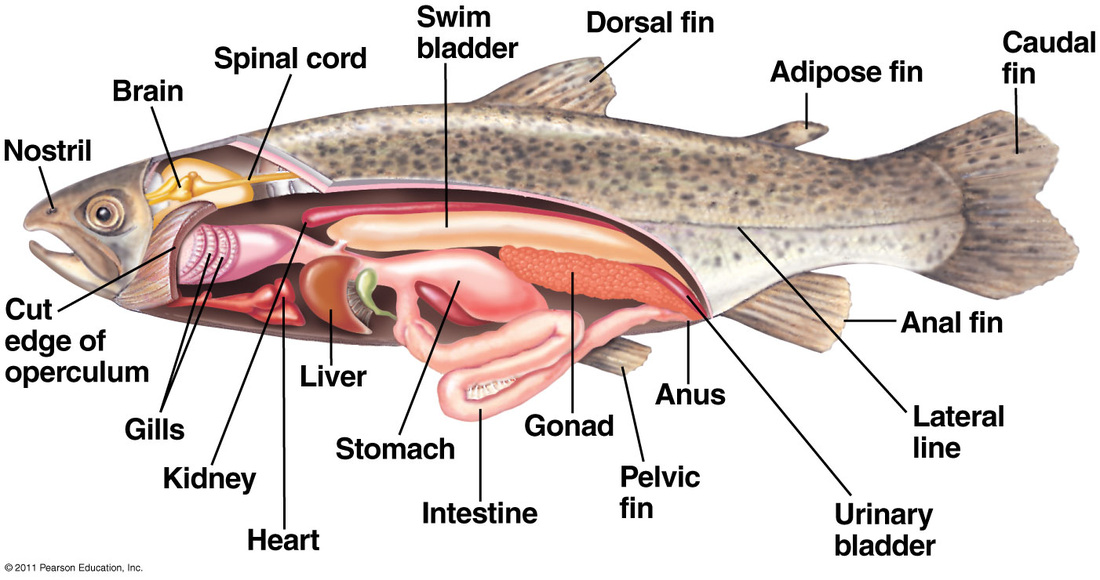
Excretory System Understanding Vertebrates
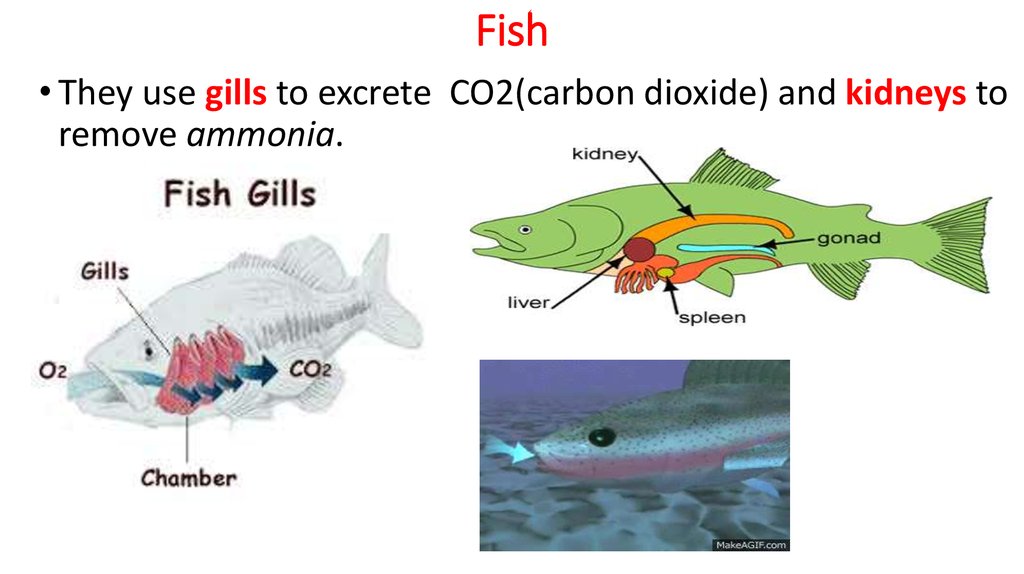
Fish utilize kidneys to filter out the wastes from their blood and then use their skin and gills to excrete nitrogenous wastes, ammonia and excess water (they rely a lot on diffusion).. It can be considered the most complex excretory system of the animals. Part of the digestive system of a fish. Homeostasis maintained by fish. Dissection.

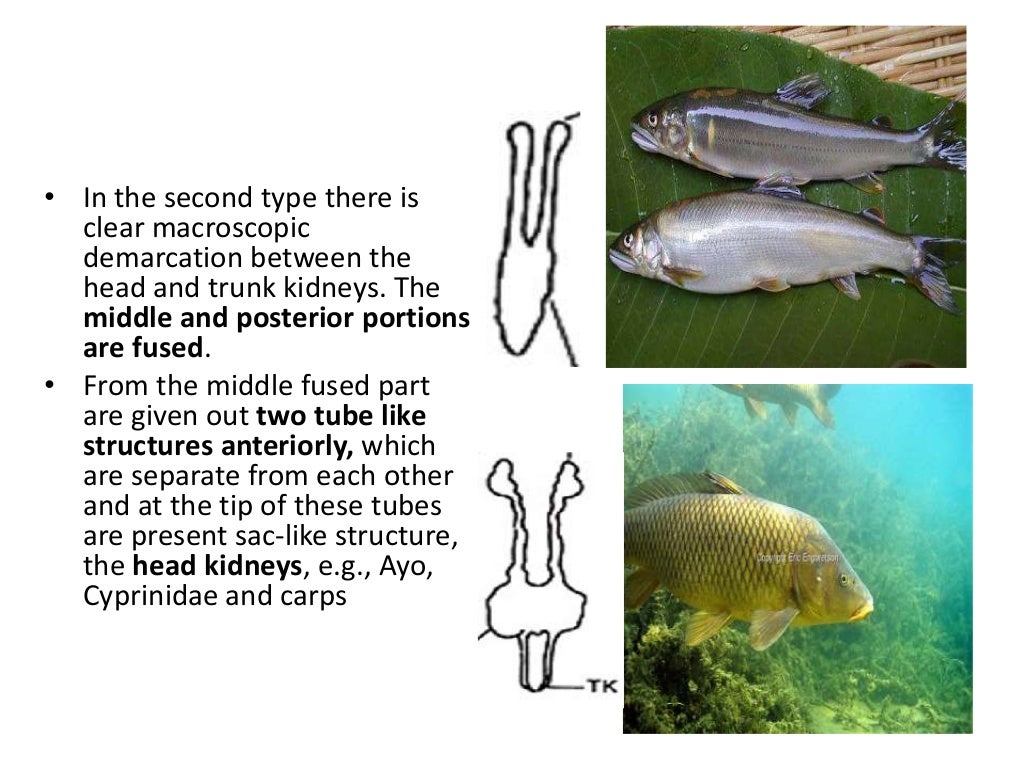
Excretory system of fishes
Gyotaku means 'fish rubbing.' Gyotaku is valued from both a scientific and artistic perspective. The detail captured in gyotaku, especially in historical prints, is an important source of information for scientists who want to know the size and external features of fish in the past.

The respiratory system Plant Natural
Agnatha (/ ˈ æ ɡ n ə θ ə, æ ɡ ˈ n eɪ θ ə /; from Ancient Greek ἀ-(a-) 'without', and γνάθος (gnáthos) 'jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both living (cyclostomes) and extinct (conodonts, anaspids, and ostracoderms) species.Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as.
excretory system
Fish excretory system . In aquatic environments, fish have developed specialized excretory structures to cope with the challenges of living in water. Their primary excretory organs are the kidneys, which regulate water and ion balance. Fish kidneys filter blood through nephrons, removing waste products and regulating electrolyte balance..

Zoology Carlson Stock Art in 2021 Circulatory system, Fish anatomy, Excretory system
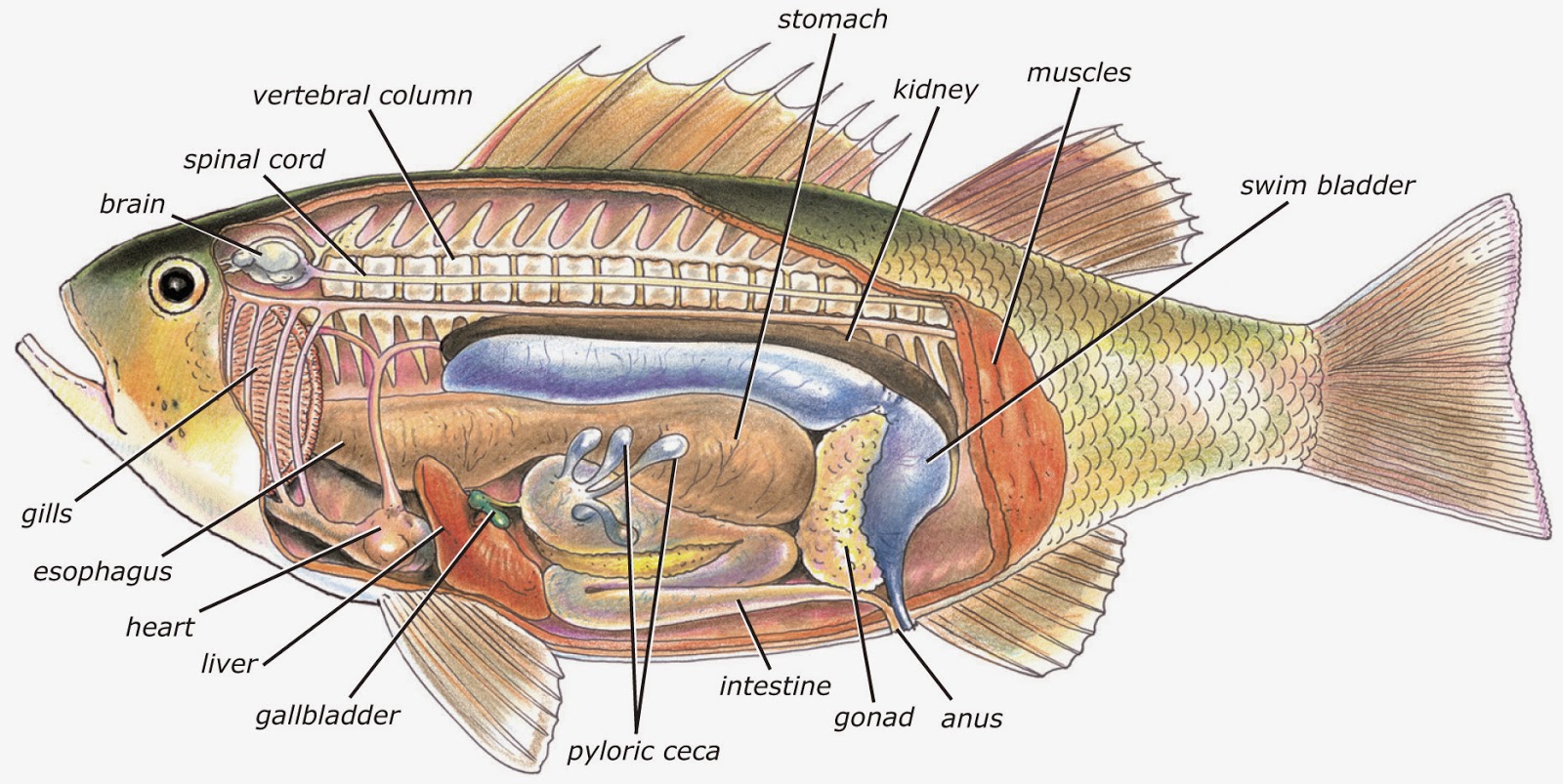
The excretory organs consist of kidneys, ureters and urinary bladder. a) Kidney: Kidneys of vertebrates are made up of nephron or kidney tubules. In ancestral vertebrates, kidney possesses one nephron for each of those body segments that lay between the anterior and posterior end of the coelom. The nephron drained into a duct called Wolffian. Excretory system of fish Read More »
Animals excretion online presentation
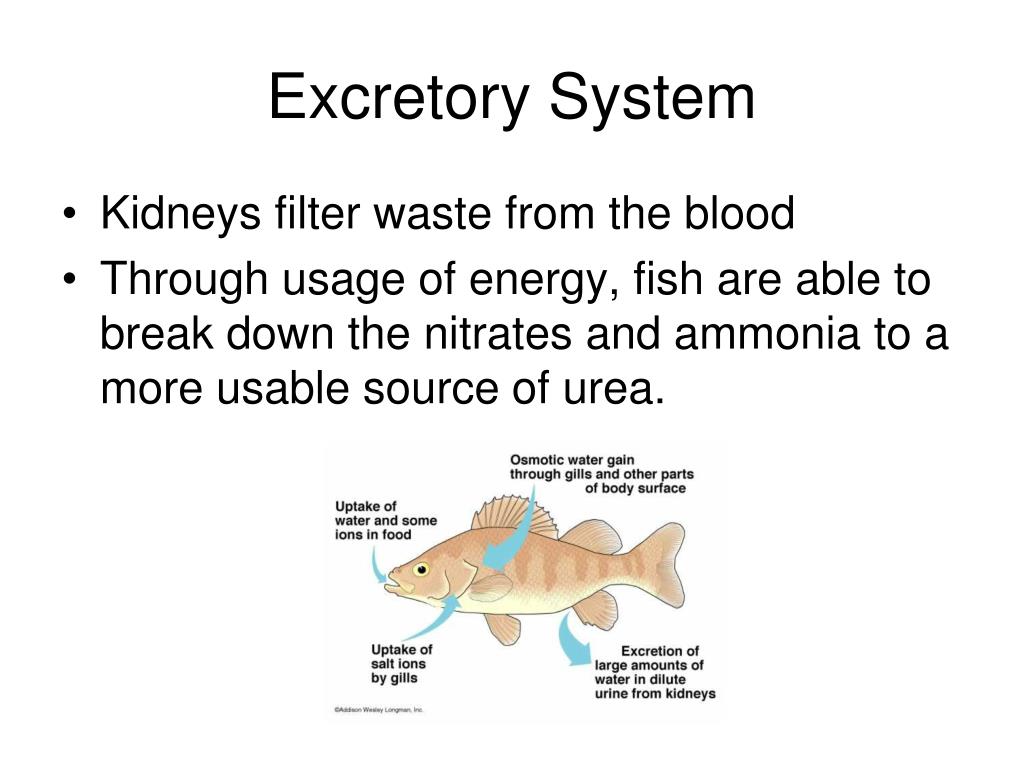
The excretory system is responsible for regulating water balance in various body fluids. Osmoregulation refers to the state aquatic animals are in: they are surrounded by freshwater and must constantly deal with the influx of water. Animals, such as crabs, have an internal salt concentration very similar to that of the surrounding ocean.

PPT Gas exchange in insects trachea PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2015796
Proper balance of the internal environment ( homeostasis) of a fish is in a great part maintained by the excretory system, especially the kidney. osmotic regulation in teleost fishes Generalized osmotic regulation in freshwater and marine teleost fishes.

Excretory system of fishes
The majority of nitrogenous waste is excreted through the gills. Kidney: Anterior / head kidney (HAEMATOPOITIC) Posterior /excretory kidney. 4. Excretory System in Fishes • In vertebrates, the excretory and reproductive organs are morphologically interrelated because certain excretory ducts are used for the discharging of gametes also.